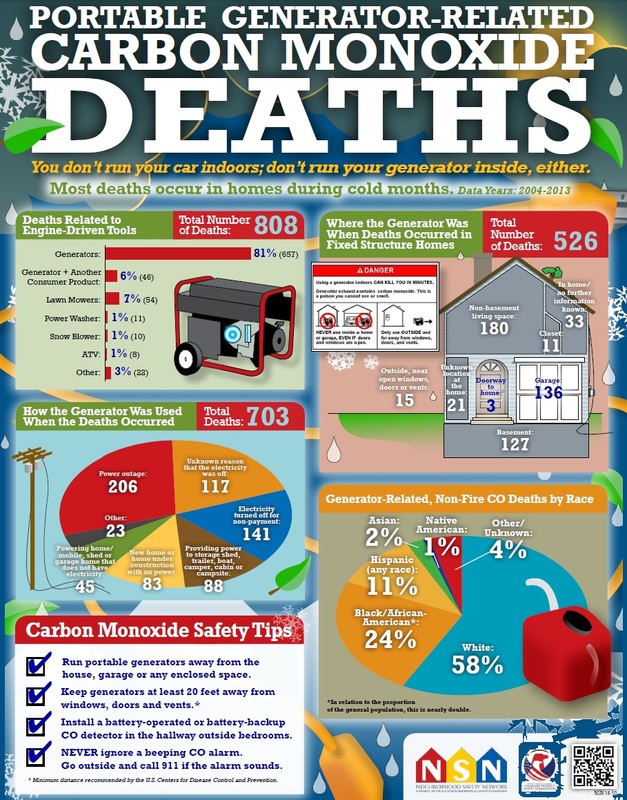
Portable Generator Safety
Portable generators are internal combustion engines used to generate electricity. They are useful when temporary or remote power is needed, and are commonly used during cleanup and recovery efforts following disasters such as hurricanes, tornadoes, etc. This fact sheet discusses specific hazards inherent with the use of generators and also provides helpful information to ensure that everyone remains safe.
Hazards Associated with Generators:
* Shocks & electrocution from improper use of power or accidentally energizing other electrical systems.
* Carbon Monoxide from a generator's exhaust.
* Fires from improperly refueling a generator or inappropriately storing fuel for a generator.
* Noise and vibration hazards.
Shock & Electrocution
The electricity created by generators has the same hazards as normal utility-supplied electricity. It also has some additional hazards because generators often bypass the safety devices (such as circuit breakers that are built into electrical systems. The following precautions should be taken to reduce shock.
* Never attach a generator directly to the electrical system of a structure (home, office, trailer, etc.) unless a qualified electrician has properly installed a generator transfer switch. Attaching a generator directly to a building electrical system can energize wiring systems for great distances. This creates a risk of electrocution for utility workers and others in the area.
* Always plug electrical appliances directly into the generator using the manufacturer's supplied cords or extension cords that are grounded (3-pronged). Inspect the cords to make sure they are fully intact and not damaged. Never use damaged or frayed cords.
* Ensure cords are appropriately rated in watts or amps for intended use. Do not use underrated cords, replace them with appropriately rated cords that use heavier gauge wire.
* Do not overload a generator, this can lead to overheating and fire.
* Use ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), especially where electrical equipment is used in a wet or damp area. GFCIs shut off power when power is detected outside normal paths. GFCIs and extension cords with built-in GFCIs can be purchased at local hardware stores. Regardless of GFCI use, electrical equipment used in wet and damp locations must be listed and approved for those locations.
* Make sure the generator is properly grounded and the grounding connections are tight. View the manufacturer's instructions for grounding.
* Keep a generator dry, do not use it in the rain or wet conditions. If needed, protect with a canopy.
* Never manipulate a generators electrical components if you are wet or standing in water.
* Do not use electrical equipment that has been submerged in water. Equipment must be thoroughly dried before using. Power off and do not use any electrical equipment that has strange odors or begins smoking.
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, toxic gas. Many people have died from CO poisoning because their generator was not properly ventilated.
* Never use a generator indoors such as enclosed spaces, garages, basements and crawl spaces.
* Do not use near open windows and doors.
* Make sure the generator has at least 3 feet of clear space on all sides and aim the exhaust AWAY from a structure.
* If you or others show symptoms of CO poisoning such as; dizziness, headaches, nausea or tiredness, get fresh air immediately and seek medical attention. Do not re-enter the structure until it is determined safe by the fire company.
Fire Hazards
* Generators become hot while running and remain hot for long periods of time after they are shut off.
* Generator fuels such as gasoline and kerosene can ignite when spilled on hot engine parts
* Before refueling, shut down the generator and allow it to cool.
* Gasoline and other fuels should be stored an transported in properly designed containers and vented.
* Keep fuel containers away from flame producing and heat generating sources such as the generator itself, cigarettes, lighters, and matches. Do not smoke around fuel containers as vapors may ignite.
* Do not store fuels in your home, store them away from living areas.
Noise & Vibration Hazards
* Generator engines vibrate and create noise. Excessive noise and vibration could cause hearing loss and vibration could cause fatigue and hearing loss.
* Keep portable generators as far away as possible from gathering spaces.
* Wear hearing protection if the generator is close by.
Hazards Associated with Generators:
* Shocks & electrocution from improper use of power or accidentally energizing other electrical systems.
* Carbon Monoxide from a generator's exhaust.
* Fires from improperly refueling a generator or inappropriately storing fuel for a generator.
* Noise and vibration hazards.
Shock & Electrocution
The electricity created by generators has the same hazards as normal utility-supplied electricity. It also has some additional hazards because generators often bypass the safety devices (such as circuit breakers that are built into electrical systems. The following precautions should be taken to reduce shock.
* Never attach a generator directly to the electrical system of a structure (home, office, trailer, etc.) unless a qualified electrician has properly installed a generator transfer switch. Attaching a generator directly to a building electrical system can energize wiring systems for great distances. This creates a risk of electrocution for utility workers and others in the area.
* Always plug electrical appliances directly into the generator using the manufacturer's supplied cords or extension cords that are grounded (3-pronged). Inspect the cords to make sure they are fully intact and not damaged. Never use damaged or frayed cords.
* Ensure cords are appropriately rated in watts or amps for intended use. Do not use underrated cords, replace them with appropriately rated cords that use heavier gauge wire.
* Do not overload a generator, this can lead to overheating and fire.
* Use ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), especially where electrical equipment is used in a wet or damp area. GFCIs shut off power when power is detected outside normal paths. GFCIs and extension cords with built-in GFCIs can be purchased at local hardware stores. Regardless of GFCI use, electrical equipment used in wet and damp locations must be listed and approved for those locations.
* Make sure the generator is properly grounded and the grounding connections are tight. View the manufacturer's instructions for grounding.
* Keep a generator dry, do not use it in the rain or wet conditions. If needed, protect with a canopy.
* Never manipulate a generators electrical components if you are wet or standing in water.
* Do not use electrical equipment that has been submerged in water. Equipment must be thoroughly dried before using. Power off and do not use any electrical equipment that has strange odors or begins smoking.
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, toxic gas. Many people have died from CO poisoning because their generator was not properly ventilated.
* Never use a generator indoors such as enclosed spaces, garages, basements and crawl spaces.
* Do not use near open windows and doors.
* Make sure the generator has at least 3 feet of clear space on all sides and aim the exhaust AWAY from a structure.
* If you or others show symptoms of CO poisoning such as; dizziness, headaches, nausea or tiredness, get fresh air immediately and seek medical attention. Do not re-enter the structure until it is determined safe by the fire company.
Fire Hazards
* Generators become hot while running and remain hot for long periods of time after they are shut off.
* Generator fuels such as gasoline and kerosene can ignite when spilled on hot engine parts
* Before refueling, shut down the generator and allow it to cool.
* Gasoline and other fuels should be stored an transported in properly designed containers and vented.
* Keep fuel containers away from flame producing and heat generating sources such as the generator itself, cigarettes, lighters, and matches. Do not smoke around fuel containers as vapors may ignite.
* Do not store fuels in your home, store them away from living areas.
Noise & Vibration Hazards
* Generator engines vibrate and create noise. Excessive noise and vibration could cause hearing loss and vibration could cause fatigue and hearing loss.
* Keep portable generators as far away as possible from gathering spaces.
* Wear hearing protection if the generator is close by.